GRE EXAM
Graduate Record Examination (GRE)
GRE General Test is an aptitude cum performance test conducted by ETS (Educational testing services), based in New Jersey, United States. GRE General Test is required to be taken by a student, if a student wishes to obtain admissions in any United States, Canadian or some European Universities. The GRE score not only determines your eligibility for admission, but also whether you will be awarded financial assistance after admission. A student is required to submit his GRE score for the admission in any of following courses:
[A] Admission in any Masters Degree Program. (Known as Post graduation in India)
[B] Admission in any Ph.D. program.
The GRE General Test measures verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, critical thinking and analytical writing skills that test takers have acquired over a long period of time and developed in the course of academic career. These skills are not related to a specific subject or field of study.
- Quantitative Reasoning— Measures the ability to understand, interpret and analyze quantitative information, solve problems using mathematical models, and apply the basic concepts of arithmetic, algebra, geometry and data analysis. There is an emphasis on quantitative reasoning skills.
- Verbal Reasoning— Measures the ability to analyze and draw conclusions from discourse, reason from incomplete data, understand multiple levels of meaning, such as literal, figurative and author’s intent, summarize text, distinguish major from minor points, understand the meanings of words, sentences and entire texts, and understand relationships among words and among concepts. There is an emphasis on complex verbal reasoning skills.
- Analytical Writing— Measures critical thinking and analytical writing skills, including the ability to articulate and support complex ideas with relevant reasons and examples, and examine claims and accompanying evidence. There is an emphasis on analytical writing skills.
Format of the GRE General Test:
| Section | Time Allowed | Description |
| 1 | 60 minutes | Analytical Writing
Essay 1: Giving one’s perspective on an issue Essay 2: Analyzing an argument (30 minutes each) |
| 1-minute break | ||
| 2 | 30 minutes | Verbal Ability
6 text completion questions 5 sentence equivalence questions 9 reading comprehensive questions |
| 1-minute break | ||
| 3 | 35 minutes | Quantitative Ability
8 quantitative comparison questions 9 discrete quantitative questions 3 data interpretation questions |
| 10-minutes break | ||
| 4 | 30 minutes | Verbal Ability
6 text completion questions 5 sentence equivalence questions 9 reading comprehensive questions |
| 1-minute beark | ||
| 5 | 35 minutes | Quantitative Ability
8 quantitative comparison questions 9 discrete quantitative questions 3 data interpretation questions |
| 1-minute break | ||
| 6 | 30 or 35 minutes | Experimental Section
A third verbal or quantitative section |
Note: The computer-based General Test is composed of Verbal Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning and Analytical Writing sections. In addition, one unidentified un-scored section (Experimental Section) may be included, and this section can appear in any position in the test after the Analytical Writing Section. Questions in the unscored section are being tested for possible use in future tests and answers will not count toward your scores.
- Total testing time is up to 3 hours 15 minutes not including the research section. The directions at the beginning of each section specify the total number of questions in the section and the time allowed for the section.
- The Analytical writing section is always first.
- The Verbal and Quantitative sections may appear in any order, including an unidentified unscored section. Treat each section presented during your test as if it counts.
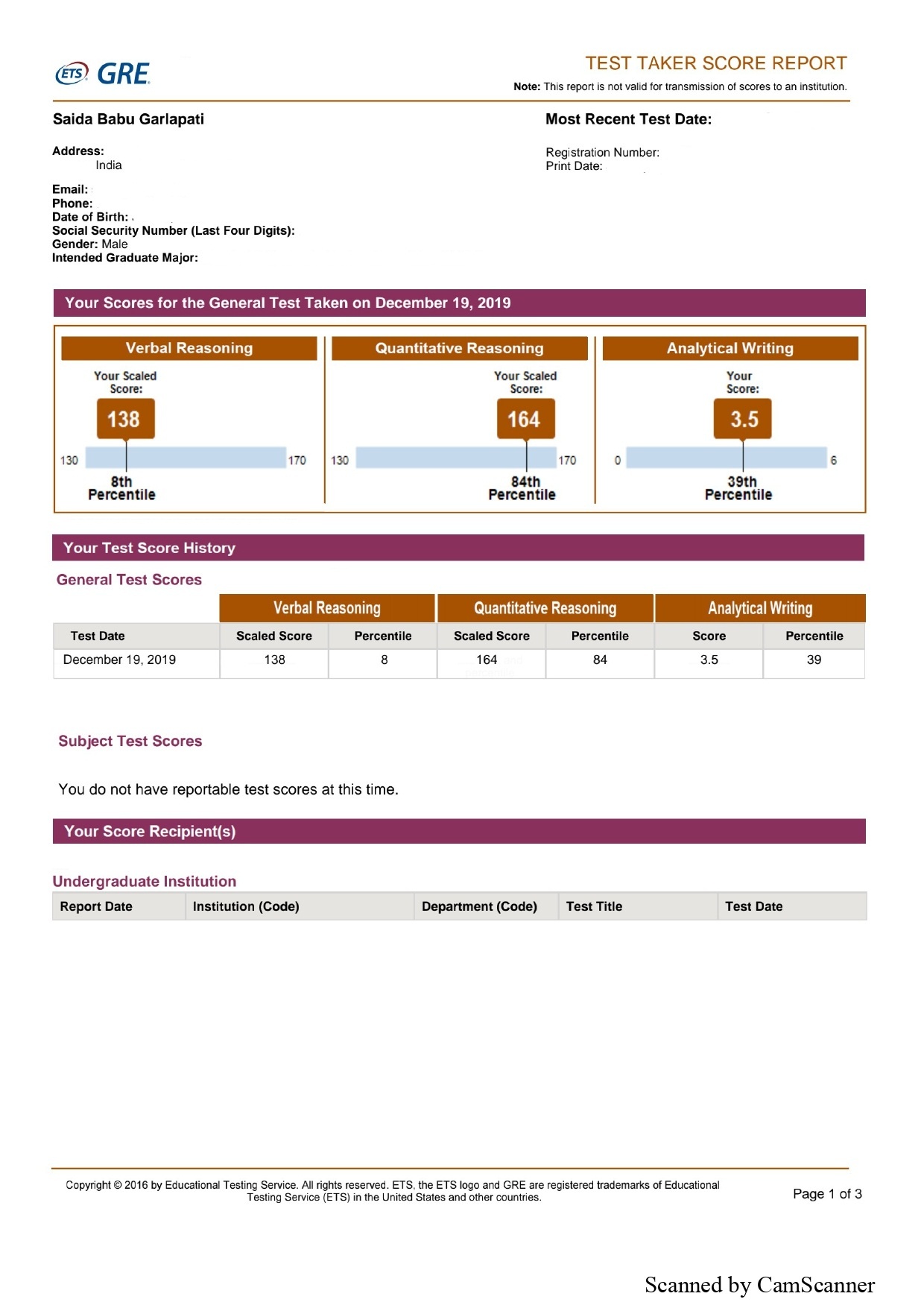
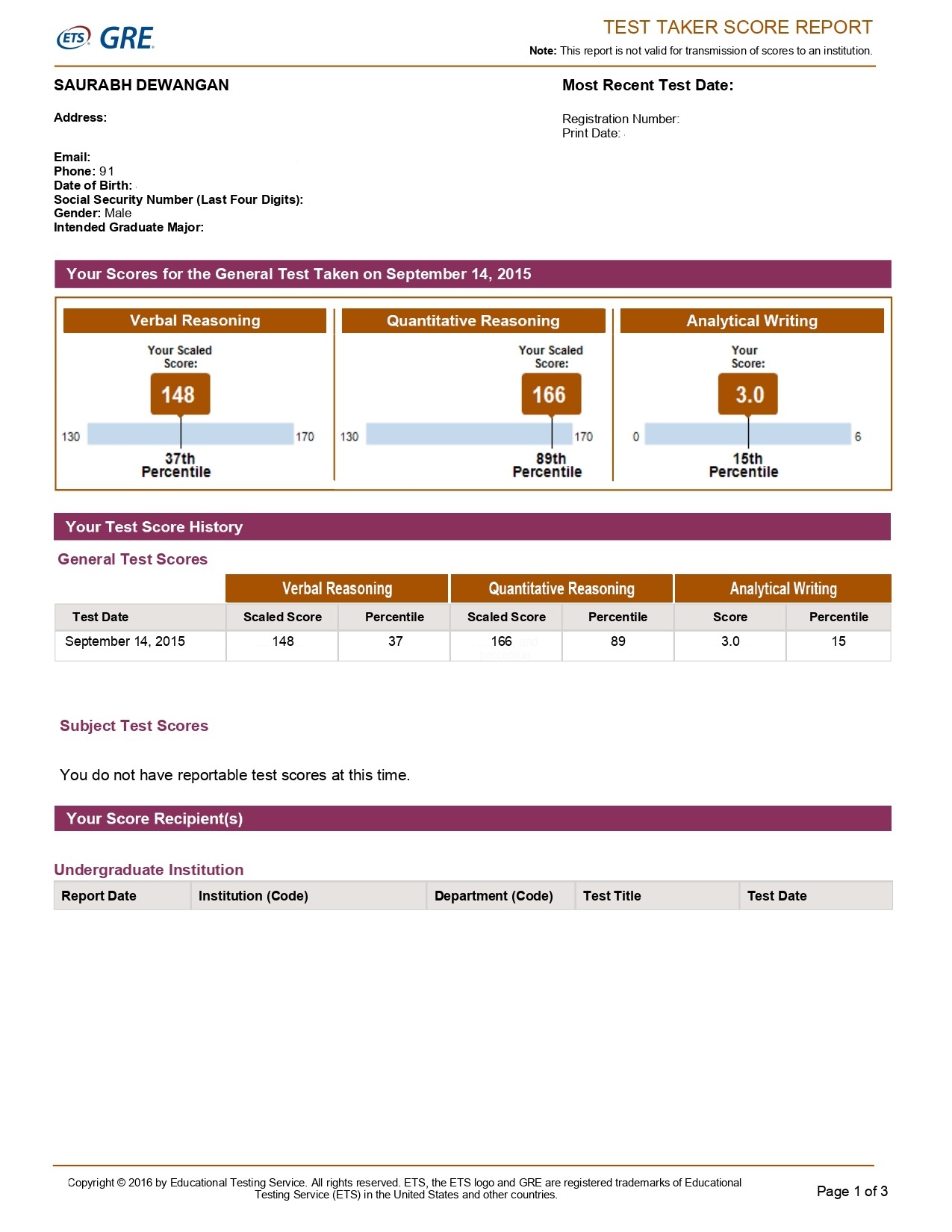
A verbal score reported on a 130-170 score scale with 1 point increment. A Quantitative score reported on a 130-170 score scale with 1 point increment. Analytical writing (AWM) score reported on 0-6 score scale, with half point increments.
Nature of the Test
The Verbal Reasoning and Quantitative Reasoning measures are section-level adaptive. This means the computer selects the second operational section of a measure based on your performance on the first section. Within each section, all questions contribute equally to the final score.
For the Analytical Writing section, each essay receives a score from at least one trained rater, using a six-point holistic scale. In holistic scoring, raters are trained to assign scores on the basis of the overall quality of an essay in response to the assigned task. The essay is then scored by e-rater®, a computerized program developed by ETS that is capable of identifying essay features related to writing proficiency. If the human and the e-rater scores closely agree, the average of the two scores is used as the final score. If they disagree, a second human score is obtained, and the final score is the average of the two human scores.
The final scores on the two essays are then averaged and rounded to the nearest half-point interval on the 0–6 score scale.
Identification Requirement:
All test takers in Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan MUST use valid passports as their ID documents.
Eligibility:
There is no eligibility requirement to take the test. Prospective MS applicants of any area of study take the General Test. Anyone with any background of any age can take the test.
GRE® test scores are used by admissions or fellowship committees to supplement Indian graduate records and other qualifications for MS study abroad. The scores provide common measures for comparing the qualifications of applicants and aid in evaluating grades and recommendations.
Score Validity:
GRE Scores are valid for the five years. However a student can take GRE General Test as many times he wants. Every new score is valid for 5 years. You will have the option to select the Most Recent score and Send your scores for up to four institutions for free at just after the exam .
Repeating the GRE General Test:
It may be to your advantage to take the GRE® General Test more than once if you think that the scores you obtained do not reflect your true abilities. If your scores seem unusually low in comparison with other indicators of your preparedness for graduate studies, you may want to consider taking the test again. Those considering repeating a test should be aware that large score increases are unusual, and for some test takers scores will go down.
A student may take the Computer Based GRE general test once per calendar month up to five times in a 12 month period. This applies even if you cancelled your scores on a test taken previously.
GRE Subject Tests:
The subject tests measures achievement in specific subject areas and assume undergraduate majors or extensive background in those disciplines. The subject test is offered in 6 subject areas as follows:
- Biology
- Chemistry
- Literature in English
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Psychology
GRE subject test questions are designed to measure skills and knowledge gained over a long period of time. Although you might increase your score to some extent through preparation a few weeks or months before you take the test, last minute cramming is unlikely to be of further help.
Who Takes Them and Why?
Prospective MS applicants take the Subject Tests. GRE test scores are used by admissions or fellowship panels to supplement graduate academic records and other qualifications for graduate study.
The scores provide common measures for comparing the qualifications of applicants and aid in the evaluation of grades and recommendations. Some Subject Tests yield sub scores that can indicate the strengths and weaknesses of individual students’ preparation and may be useful for guidance and placement purposes.